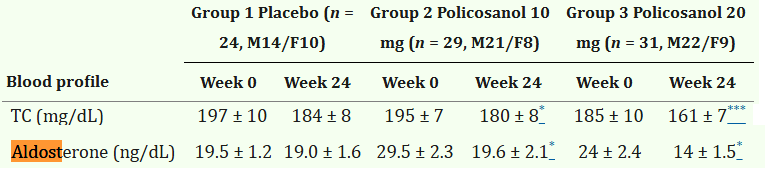Continued from
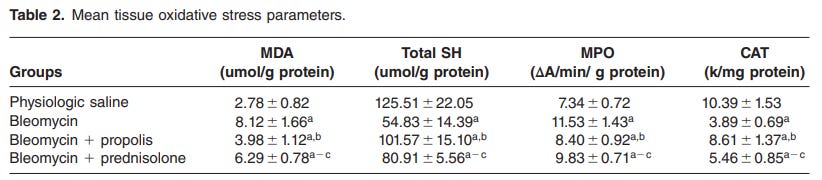
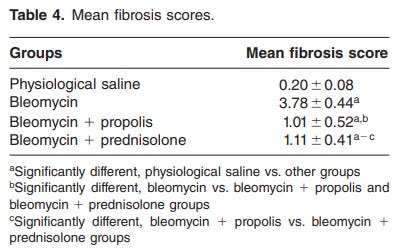
Propolis worked slightly better for preventing lung fibrosis than corticosteroids (prednisolone), in a bleomycin model, and likely has much fewer side effects
(fibrosis = excessive connective tissue depositing where it shouldn’t be) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26960158/
Although the mean fibrosis scores of the bleomycin propolis and bleomycin prednisolone groups were not significantly different, electron microscopy revealed that propolis diminished bleomycin induced lung fibrosis more effectively than prednisolone
100mg/kg in rats orally. A 1g - 2g human dose might be effective, but it depends on enzyme differences.
putting propolis gel on cold sores a few times a day can be effective
It has an anti viral effect against herpes in cell studies, and worked here to improve lesion healing. 6.2 days vs 9.7 days for placebo
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286724416
It outperforms the antiviral medication acyclovir in other studies.
Vitamin C is very protective against radiation. It’s effective against both forms, ionising forms like X-rays and non-ionising e.g ultrasound / wifi / mobile, electronics.
non ionising (mobile phone)
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02850217
ionising
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4479387/
It helps prevent radiation-induced damages: “cell death, DNA double-strand breaks, lipid peroxidation, and protein carbonylation”.
The researchers also found you can use it after and still get the protection, so still useful if can’t take it before high exposure.
Ray peat talked about a study where frogs were given red light a while after being irradiated and it was still protective.
“Our findings confirm the results obtained in our previous study which investigated the survival rate in animals received vitamin C 1h, 12h and 24h after irradiation. This study showed that vitamin C can potentially be used up to 24 hours after exposure to high levels of ionizing radiation in life threatening situations such as unpredictable solar particle events.
The damaging effects of a burst of radiation can linger for a while.
blood counts stayed depressed for 3 days before showing signs of recovery (or for higher doses of radiation, they dont recover from here).
Post treatment with a good amount of vit C for 3 days is needed to get a fuller protective effect
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3821576/
Omitting post-treatment from the combination therapy with ascorbic acid markedly reduced the mouse survival (20% survival), suggesting the importance of post-treatment with ascorbic acid. Combination therapy with ascorbic acid may be a potent therapeutic tool for radiation-induced gastrointestinal damage.
However, combination therapy using ascorbic acid, including pretreatment, engulfment and post-treatment, rescued all of the mice from lethal abdominal radiation, and was accompanied by remarkable improvements in the gastrointestinal damage (100% survival).
Having a gram of vitamin C every day seems excessive,
some problems can occur with lower ceruloplasmin potentially, and some minerals might be excreted excessively (going by that & lead being reduced a lot at a 1g dose in humans vs 200mg).
It can also lower hif-1a which can be helpful against many tumors, but needed for some functions e.g wound healing.
Maybe a good approach if having an X-ray or an ultrasound / scan is taking a boost of 200mg-1g vitamin C for 3 days.
(& generally hitting 100mg daily through food for some protection from an ongoing low level of electronics radiation).
(also applies to bursts of sun damage / high UV exposure from solar events, or space travel in the future)
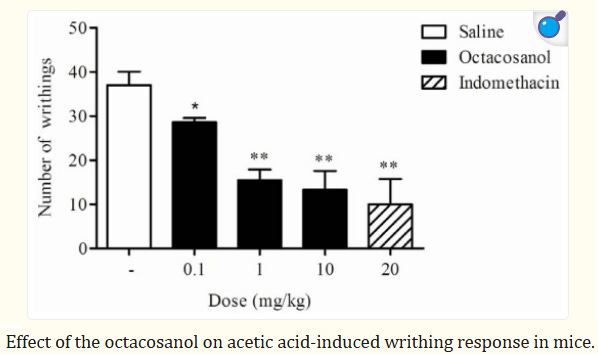
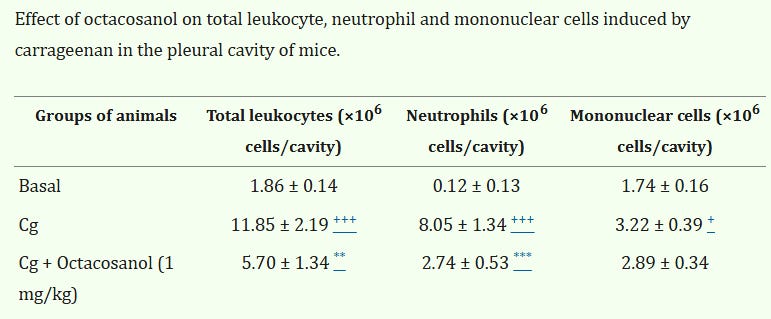
Octacosanol is an effective anti inflammatory substance / pain reliever
(for inflammatory pain, not neuropathic) and can lower atherosclerosis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22408410/
interestingly it can also end a THC high?
*things to be aware of:
- I dont know if there’s a rebound problem with this / potential for more pain after stopping, that idea is just speculating though.
- It also inhibits VEGF, which is needed to heal wounds, a little might not be a problem, but something to be aware of if someone has a chronic wound. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299908003956
- It has effect at the Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor, so can have a sedative property at higher doses
- It lowers cholesterol
Policosanol, which can contain octacosanol as a main compound if formulated well, showed a reduction of aldosterone in humans.
(aldosterone can contribute to edema sometimes, it increases blood pressure and ray peat said elevations cause fibrosis and inflammation in the heart.
people restricting sodium too much get elevated aldosterone which starts when you drop below ~5g of salt a day, recommendations are set lower, ironically probably making heart disease worse from elevating aldosterone. which is probably why low salt intake associates with higher death rates)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5939616/
A lot of the studies on atherosclerosis come from cuba, but this was a korean government study
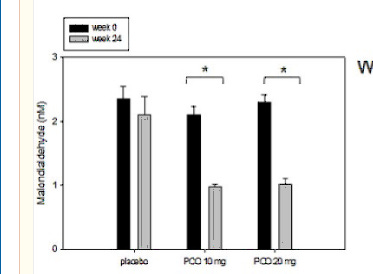
It lowered oxidative stress well, less MDA. and cholesterol came down (likely from lower inflammation)
and prevented brain inflammation very well in mice given orally, with a big protective effect on brain function.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8389325/
Some studies show a potent lowering of cholesterol by this. with 10mg - 40mg as policosanol showing similar effect as a ~-15% drop in total and up to ~30% drop in LDL.
https://altmedrev.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/v7-3-203.pdf
High cholesterol isn’t the main core problem to be targeting for heart health, its largely an outcome of hypothyroidism and / or inflammation. the thyroid hormone T3 lowers cholesterol well.
2 of the main factors in heart disease are hypothyroidism and inflammation, with cholesterol traveling to sites of inflammation and macrophages in inflamed arteries engulfing it.
Cholesterol has beneficial effects in the body, playing a role in immunity and myelin repair in the brain. It’s used for hormone production.
So i wondered if using this daily instead of acute situations could be a problem with someone who doesn’t have elevated cholesterol.
It has a different mechanism for lowering cholesterol than statins, being an indirect effect, and increasing LDL receptors, rather than a direct effect as the full pathway blocking with statins
(which have shown significant hormone reduction at certain doses, a minority % of cholesterol is used for hormone synthesis, but statins effect on hormones is largely due to them also depleting isoprenoids in the mevalonate pathway, needed for steroidogenic enzymes).
(its metabolised to a very long chain fatty acid)
Octacosanol doesn’t act via blocking the mevalonate pathway potently , shown here in humans (their coq10 levels actually went up, statins deplete)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10820701/#sec2-pharmaceuticals-17-00132
Octacosanol (in birds) increased reproductive hormones https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032579119316098?via%3Dihub#cesec80
HDL is the major source of cholesterol for creating hormones in the testis. and Policosanol (if high in octacosanol) increases HDL.
Extracted from sugarcane wax is best as it’s the freeform which we absorb well. Ester forms from honeycomb / beeswax don’t break down properly in our gut.
Atherosclerosis
6 of 11 people had functional regression of their atherosclerosis on policosanol with a low fat diet. only 1 of the 11 had progression. the low fat diet probably helped enhance things too as some in the other group got regression.
and if you look at the vertebral artery area 8 out of 11 in the policosanol group got regression. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0011393X95850945
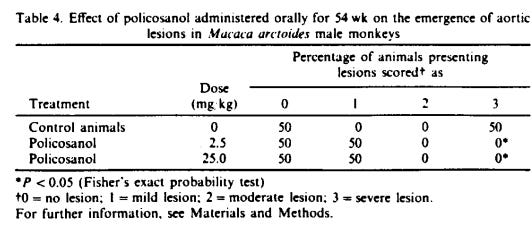
In monkeys 50% of them had severe lesions in their arteries as they aged. In the policosanol group, none of them did. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8045464/
Statins are unimpressive. As a mainstream standard they aren’t effective enough to treat this. They’re prescribed to slow progression, meaning disease isn’t being fixed, and to apparently stabilize plaques with only a small absolute % difference on death outcomes if that’s shown, and increased muscle dysfunction with that. https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.04.015
they aren’t given to create remission / regression / to heal from disease.
And their main effect for what they do give is largely due to their inflammation lowering property, regardless of effects on cholesterol.
I would guess high cholesterol doesn’t help, but researchers gave mice a statin where the animals were altered to be mostly unresponsive to the cholesterol lowering aspect, and the statins still showed the effect of lower cholesterol in arteries without significantly lowering general cholesterol.
They found statins have anti-inflammatory effects, so it indicates the main effect of statins is through the lowering of inflammation, not mainly from lowering cholesterol.
(took a probably high dose to show the numbers quoted)
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.ATV.21.1.115
(atherosclerosis is primarily an inflammation problem not a cholesterol problem. (and before that, maybe a mitochondria problem). and the high cholesterol commonly indicates low thyroid hormone, which is also key for heart function)
We confirm that simvastatin is anti-inflammatory by using a classic model of inflammation. Simvastatin was comparable to indomethacin in this model.
To determine whether the anti-inflammatory activity of simvastatin might affect atherogenesis, simvastatin was tested in mice deficient in apoE.
Mice were dosed daily for 6 weeks with simvastatin (100 mg/kg body wt). Simvastatin did not alter plasma lipids. Atherosclerosis was quantified through the measurement of aortic cholesterol content. Aortas from control mice (n=20) contained 56±4 nmol total cholesterol/mg wet wt tissue, 38±2 nmol free cholesterol/mg, and 17±2 nmol cholesteryl ester/mg. Simvastatin (n=22) significantly (P<0.02) decreased these 3 parameters by 23%, 19%, and 34%, respectively.
Histology of the atherosclerotic lesions showed that simvastatin did not dramatically alter lesion morphology. These data support the hypothesis that simvastatin has antiatherosclerotic activity beyond its plasma cholesterol–lowering activity.
Policosanol combined with lot fat was more effective, helping to give remission. probably in large part due to its inflammation effect.
It also inhibits vascular calcification well, and outperformed a statin here, along with improved anti inflammatory effect
(another non cuban study)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5068461/#sec8-1535370216659943
and here in humans, with less side effects
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10939029/
As shown earlier statins do more than blocking cholesterol only, ubiquinol goes down too as its in the same pathway, which is important for our mitochondria function. so if taking statins supplementing ubiquinone might be a good idea to help restore levels.
(ubiquinone is better absorbed than ubiquinol and raises ubiquinol levels more). aging tissues already show lower levels so it could compound things.
Also, why is cholesterol elevated to begin with? what are the core common dysfunctions here?
"genetics" is a dismissive way to explain away something without knowing more details, it can apply to certain diseases or individuals with rare mutations, but this is a very broad problem applying to many,
there is a significant link between low thyroid hormone and atherosclerosis. Check this study out https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7760967/ where giving people T3 normalised their high cholesterol with a big drop. Its the bodies way of lowering cholesterol.
They were studied 2 weeks after withdrawal of triiodothyronine (T3) therapy and 7 (5-9) weeks after resumption of T3 treatment. Apo B and LDL cholesterol fell by 42% (p < 0.001) and by 53% (p < 0.001), respectively.
So high cholesterol might commonly be indicating insufficient t3 levels. (aka hypothyroidism)
I think octacosanol could come in useful as a pain reliever in extreme situations ~20mg - 40mg, and as a decent anti inflammatory substance.
1 question I have left over is effects on immunity taking daily.
If using a high dose it’s probably not suitable for daytime use with its potential for some sedation unless someone isnt very active. (But i think it made my already vivid dreams even more vivid taken in the hours leading into sleep. I had a wild lucid dream where i couldn’t walk or talk properly in it, stumbling everywhere, and a scientist was electrocuting me until I could shout again. but cant be sure it was this, my dreaming is overactive generally).
Maltodextrin (if used in carb replacement amounts) creates low level inflammation & more susceptibility to intestinal damage, through mucin depletion & causing ER stress
https://www.cmghjournal.org/article/S2352-345X(18)30121-8/fulltext
the lowest amount at 1% in their drinking water didnt have the effect (e.g 10g per liter of water through the day) but 3% did. So where small amounts shouldn’t be a problem, doesnt look like a good option for a carb source.
(the bile acid TUDCA helps reverse the damage. tudca has a wakefulness promoting property for a few hours through the histamine receptor, but inhibits gaba signalling a bit. It’s potent at lowering ER stress which causes apoptosis (cell death) through a buildup of proteins that aren’t folding correctly in cells. long term it might have carcinogenic property in the stomach if taken with food or low acidity, so maybe best without food if taking it for ER stress).